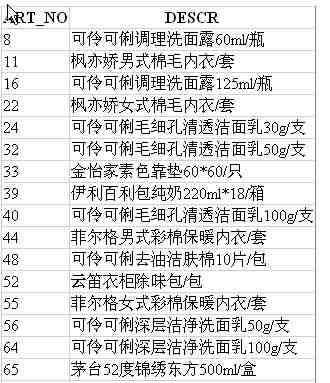
|
|
先了解一下IIS系統(tǒng)。它是一個程序,負責(zé)對網(wǎng)站的內(nèi)容進行管理并且處理對客戶的請求做出反應(yīng)。當(dāng)用戶對一個頁面提出請求時,IIS做如下反應(yīng)(不考慮權(quán)限問題):
1.把對方請求的虛擬路徑轉(zhuǎn)換成物理路徑
2.根據(jù)物理路徑搜索請求的文件
3.找到文件后,獲取文件的內(nèi)容
4.生成Http頭信息。
5.向客戶端發(fā)送所有的文件內(nèi)容:首先是頭信息,然后是Html內(nèi)容,最后是其它文件的內(nèi)容。
6.客戶端IE瀏覽器獲得信息后,解析文件內(nèi)容,找出其中的引用文件,如.js .css .gif等,向IIS請求這些文件。
7.IIS獲取請求后,發(fā)送文件內(nèi)容。
8.當(dāng)瀏覽器獲取所有內(nèi)容后,生成內(nèi)容界面,客戶就看到圖像/文本/其它內(nèi)容了。
但是IIS本身是不支持動態(tài)頁面的,也就是說它僅僅支持靜態(tài)html頁面的內(nèi)容,對于如.ASP,.ASPx,.cgi,.php等,IIS并不會處理這些標(biāo)記,它就會把它當(dāng)作文本,絲毫不做處理發(fā)送到客戶端。為了解決這個問題。IIS有一種機制,叫做ISAPI的篩選器,這個東西是一個標(biāo)準(zhǔn)組件(COM組件),當(dāng)在在訪問IIS所不能處理的文件時,如ASP.NET 1.1 中的IIS附加ISAPI篩選器如圖:
ASP.NET 服務(wù)在注冊到IIS的時候,會把每個擴展可以處理的文件擴展名注冊到IIS里面(如:*.ascx、*.ASPx等)。擴展啟動后,就根據(jù)定義好的方式來處理IIS所不能處理的文件,然后把控制權(quán)跳轉(zhuǎn)到專門處理代碼的進程中。讓這個進程開始處理代碼,生成標(biāo)準(zhǔn)的HTML代碼,生成后把這些代碼加入到原有的 Html中,最后把完整的Html返回給IIS,IIS再把內(nèi)容發(fā)送到客戶端。
有上面對ISAPI的簡單描述,我們把HttpModule& HttpHandler分開討論,并且結(jié)合CS進行具體的實現(xiàn)分析。
HttpModule:
HttpModule實現(xiàn)了ISAPI Filter的功能,是通過對IhttpModule接口的繼承來處理。下面打開CS中的CommunityServerComponents項目下的CSHttpModule.cs文件(放在HttpModule目錄)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// <copyright company="Telligent Systems">
// Copyright (c) Telligent Systems Corporation. All rights reserved.
// </copyright>
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Web;
using CommunityServer.Components;
using CommunityServer.Configuration;
namespace CommunityServer
{
// *********************************************************************
// CSHttpModule
//
/**//// <summary>
/// This HttpModule encapsulates all the forums related events that occur
/// during ASP.NET application start-up, errors, and end request.
/// </summary>
// ***********************************************************************/
public class CSHttpModule : IHttpModule
{
Member variables and inherited properties / methods#region Member variables and inherited properties / methods
public String ModuleName
{
get { return "CSHttpModule"; }
}
// *********************************************************************
// ForumsHttpModule
//
/**//// <summary>
/// Initializes the HttpModule and performs the wireup of all application
/// events.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="application">Application the module is being run for</param>
public void Init(HttpApplication application)
{
// Wire-up application events
//
application.BeginRequest += new EventHandler(this.Application_BeginRequest);
application.AuthenticateRequest += new EventHandler(Application_AuthenticateRequest);
application.Error += new EventHandler(this.Application_OnError);
application.AuthorizeRequest += new EventHandler(this.Application_AuthorizeRequest);
//settingsID = SiteSettingsManager.GetSiteSettings(application.Context).SettingsID;
Jobs.Instance().Start();
//CSException ex = new CSException(CSExceptionType.ApplicationStart, "Appication Started " + AppDomain.CurrentDomain.FriendlyName);
//ex.Log();
}
//int settingsID;
public void Dispose()
{
//CSException ex = new CSException(CSExceptionType.ApplicationStop, "Application Stopping " + AppDomain.CurrentDomain.FriendlyName);
//ex.Log(settingsID);
Jobs.Instance().Stop();
}
Installer#region Installer
#endregion
#endregion
Application OnError#region Application OnError
private void Application_OnError (Object source, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application = (HttpApplication)source;
HttpContext context = application.Context;
CSException csException = context.Server.GetLastError() as CSException;
if(csException == null)
csException = context.Server.GetLastError().GetBaseException() as CSException;
try
{
if (csException != null)
{
switch (csException.ExceptionType)
{
case CSExceptionType.UserInvalidCredentials:
case CSExceptionType.AccessDenied:
case CSExceptionType.AdministrationAccessDenied:
case CSExceptionType.ModerateAccessDenied:
case CSExceptionType.PostDeleteAccessDenied:
case CSExceptionType.PostProblem:
case CSExceptionType.UserAccountBanned:
case CSExceptionType.ResourceNotFound:
case CSExceptionType.UserUnknownLoginError:
case CSExceptionType.SectionNotFound:
csException.Log();
break;
}
}
else
{
Exception ex = context.Server.GetLastError();
if(ex.InnerException != null)
ex = ex.InnerException;
csException = new CSException(CSExceptionType.UnknownError, ex.Message, context.Server.GetLastError());
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlException sqlEx = ex as System.Data.SqlClient.SqlException;
if(sqlEx == null || sqlEx.Number != -2) //don't log time outs
csException.Log();
}
}
catch{} //not much to do here, but we want to prevent infinite looping with our error handles
CSEvents.CSException(csException);
}
#endregion
Application AuthenticateRequest#region Application AuthenticateRequest
private void Application_AuthenticateRequest(Object source, EventArgs e)
{
HttpContext context = HttpContext.Current;
Provider p = null;
ExtensionModule module = null;
// If the installer is making the request terminate early
if (CSConfiguration.GetConfig().AppLocation.CurrentApplicationType == ApplicationType.Installer) {
return;
}
// Only continue if we have a valid context
//
if ((context == null) || (context.User == null))
return;
try
{
// Logic to handle various authentication types
//
switch(context.User.Identity.GetType().Name.ToLower())
{
// Microsoft passport
case "passportidentity":
p = (Provider) CSConfiguration.GetConfig().Extensions["PassportAuthentication"];
module = ExtensionModule.Instance(p);
if(module != null)
module.ProcessRequest();
else
goto default;
break;
// Windows
case "windowsidentity":
p = (Provider) CSConfiguration.GetConfig().Extensions["WindowsAuthentication"];
module = ExtensionModule.Instance(p);
if(module != null)
module.ProcessRequest();
else
goto default;
break;
// Forms
case "formsidentity":
p = (Provider) CSConfiguration.GetConfig().Extensions["FormsAuthentication"];
module = ExtensionModule.Instance(p);
if(module != null)
module.ProcessRequest();
else
goto default;
break;
// Custom
case "customidentity":
p = (Provider) CSConfiguration.GetConfig().Extensions["CustomAuthentication"];
module = ExtensionModule.Instance(p);
if(module != null)
module.ProcessRequest();
else
goto default;
break;
default:
CSContext.Current.UserName = context.User.Identity.Name;
break;
}
}
catch( Exception ex )
{
CSException forumEx = new CSException( CSExceptionType.UnknownError, "Error in AuthenticateRequest", ex );
forumEx.Log();
throw forumEx;
}
// // Get the roles the user belongs to
// //
// Roles roles = new Roles();
// roles.GetUserRoles();
}
#endregion
Application AuthorizeRequest#region Application AuthorizeRequest
private void Application_AuthorizeRequest (Object source, EventArgs e) {
if (CSConfiguration.GetConfig().AppLocation.CurrentApplicationType == ApplicationType.Installer)
{
//CSContext.Create(context);
return;
}
HttpApplication application = (HttpApplication)source;
HttpContext context = application.Context;
CSContext csContext = CSContext.Current;
//bool enableBannedUsersToLogin = CSContext.Current.SiteSettings.EnableBannedUsersToLogin;
// // If the installer is making the request terminate early
// if (csContext.ApplicationType == ApplicationType.Installer) {
// return;
// }
//csContext.User = CSContext.Current.User;
CSEvents.UserKnown(csContext.User);
ValidateApplicationStatus(csContext);
// Track anonymous users
//
Users.TrackAnonymousUsers(context);
// Do we need to force the user to login?
//
if (context.Request.IsAuthenticated)
{
string username = context.User.Identity.Name;
if (username != null)
{
string[] roles = CommunityServer.Components.Roles.GetUserRoleNames(username);
if (roles != null && roles.Length > 0)
{
csContext.RolesCacheKey = string.Join(",",roles);
}
}
}
}
#endregion
Application BeginRequest#region Application BeginRequest
private void Application_BeginRequest(Object source, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application = (HttpApplication)source;
HttpContext context = application.Context;
CSConfiguration config = CSConfiguration.GetConfig();
// If the installer is making the request terminate early
if (config.AppLocation.CurrentApplicationType == ApplicationType.Installer)
{
//CSContext.Create(context);
return;
}
CheckWWWStatus(config,context);
CSContext.Create(context, ReWriteUrl(context));
}
private void CheckWWWStatus(CSConfiguration config, HttpContext context)
{
if(config.WWWStatus == WWWStatus.Ignore)
return;
const string withWWW = "http://www.";
const string noWWW = "http://";
string rawUrl = context.Request.Url.ToString().ToLower();
bool isWWW = rawUrl.StartsWith(withWWW);
if(config.WWWStatus == WWWStatus.Remove && isWWW)
{
context.Response.Redirect(rawUrl.Replace(withWWW, noWWW));
}
else if(config.WWWStatus == WWWStatus.Require && !isWWW)
{
context.Response.Redirect(rawUrl.Replace(noWWW, withWWW));
}
}
ReWriteUrl#region ReWriteUrl
private bool ReWriteUrl(HttpContext context)
{
// we're now allowing each individual application to be turned on and off individually. So before we allow
// a request to go through we need to check if this product is disabled and the path is for the disabled product,
// if so we display the disabled product page.
//
// I'm also allowing the page request to go through if the page request is for an admin page. In the past if you
// disabled the forums you were locked out, now with this check, even if you're not on the same machine but you're accessing
// an admin path the request will be allowed to proceed, where the rest of the checks will ensure that the user has the
// permission to access the specific url.
// Url Rewriting
//
//RewriteUrl(context);
string newPath = null;
string path = context.Request.Path;
bool isReWritten = SiteUrls.RewriteUrl(path,context.Request.Url.Query,out newPath);
//very wachky. The first call into ReWritePath always fails with a 404.
//calling ReWritePath twice actually fixes the probelm as well. Instead,
//we use the second ReWritePath overload and it seems to work 100%
//of the time.
if(isReWritten && newPath != null)
{
string qs = null;
int index = newPath.IndexOf('?');
if (index >= 0)
{
qs = (index < (newPath.Length - 1)) ? newPath.Substring(index + 1) : string.Empty;
newPath = newPath.Substring(0, index);
}
context.RewritePath(newPath,null,qs);
}
return isReWritten;
}
#endregion
private void ValidateApplicationStatus(CSContext cntx)
{
if(!cntx.User.IsAdministrator)
{
string disablePath = null;
switch(cntx.Config.AppLocation.CurrentApplicationType)
{
case ApplicationType.Forum:
if(cntx.SiteSettings.ForumsDisabled)
disablePath = "ForumsDisabled.htm";
break;
case ApplicationType.Weblog:
if(cntx.SiteSettings.BlogsDisabled)
disablePath = "BlogsDisabled.htm";
break;
case ApplicationType.Gallery:
if(cntx.SiteSettings.GalleriesDisabled)
disablePath = "GalleriesDisabled.htm";
break;
case ApplicationType.GuestBook:
if(cntx.SiteSettings.GuestBookDisabled)
disablePath = "GuestBookDisabled.htm";
break;
case ApplicationType.Document: //新增 ugoer
if(cntx.SiteSettings.DocumentDisabled)
disablePath = "DocumentsDisabled.htm";
break;
}
if(disablePath != null)
{
string errorpath = cntx.Context.Server.MapPath(string.Format("~/Languages/{0}/errors/{1}",cntx.Config.DefaultLanguage,disablePath));
using(StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(errorpath))
{
string html = reader.ReadToEnd();
reader.Close();
cntx.Context.Response.Write(html);
cntx.Context.Response.End();
}
}
}
}
#endregion
}
}
在Web.Config中的配置:
<httpModules>
<add name="CommunityServer" type="CommunityServer.CSHttpModule, CommunityServer.Components" />
<add name="Profile" type="Microsoft.ScalableHosting.Profile.ProfileModule, MemberRole, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b7c773fb104e7562"/>
<add name="RoleManager" type="Microsoft.ScalableHosting.Security.RoleManagerModule, MemberRole, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b7c773fb104e7562" />
</httpModules>
CSHttpModule.cs UML:
要實現(xiàn)HttpModule功能需要如下步驟:
1.編寫一個類,實現(xiàn)IhttpModule接口
2.實現(xiàn)Init 方法,并且注冊需要的方法
3.實現(xiàn)注冊的方法
4.實現(xiàn)Dispose方法,如果需要手工為類做一些清除工作,可以添加Dispose方法的實現(xiàn),但這不是必需的,通常可以不為Dispose方法添加任何代碼。
5.在Web.config文件中,注冊您編寫的類
到這里我們還需要了解一個ASP.NET的運行過程:
在圖中第二步可以看到當(dāng)請求開始的時候,馬上就進入了HttpModule,在CS中由于實現(xiàn)了HttpModule的擴展CSHttpModule.cs 類,因此當(dāng)一個web請求發(fā)出的時候(如:一個用戶訪問他的blog),CS系統(tǒng)首先調(diào)用CSHttpModule.cs類,并且進入
public void Init(HttpApplication application)
該方法進行初始化事件:
application.BeginRequest += new EventHandler(this.Application_BeginRequest);
application.AuthenticateRequest += new EventHandler(Application_AuthenticateRequest);
application.Error += new EventHandler(this.Application_OnError);
application.AuthorizeRequest += new EventHandler(this.Application_AuthorizeRequest);
有事件就要有對應(yīng)的處理方法:
private void Application_BeginRequest(Object source, EventArgs e)
private void Application_AuthenticateRequest(Object source, EventArgs e)
private void Application_OnError (Object source, EventArgs e)
private void Application_AuthorizeRequest (Object source, EventArgs e)
事件被初始化后就等待系統(tǒng)的觸發(fā),請求進入下一步此時系統(tǒng)觸發(fā)Application_BeginRequest事件,事件處理內(nèi)容如下:
private void Application_BeginRequest(Object source, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application = (HttpApplication)source;
HttpContext context = application.Context;
CSConfiguration config = CSConfiguration.GetConfig();
// If the installer is making the request terminate early
if (config.AppLocation.CurrentApplicationType == ApplicationType.Installer)
{
//CSContext.Create(context);
return;
}
CheckWWWStatus(config,context);
CSContext.Create(context, ReWriteUrl(context));
}
private void CheckWWWStatus(CSConfiguration config, HttpContext context)
{
if(config.WWWStatus == WWWStatus.Ignore)
return;
const string withWWW = "http://www.";
const string noWWW = "http://";
string rawUrl = context.Request.Url.ToString().ToLower();
bool isWWW = rawUrl.StartsWith(withWWW);
if(config.WWWStatus == WWWStatus.Remove && isWWW)
{
context.Response.Redirect(rawUrl.Replace(withWWW, noWWW));
}
else if(config.WWWStatus == WWWStatus.Require && !isWWW)
{
context.Response.Redirect(rawUrl.Replace(noWWW, withWWW));
}
}
ReWriteUrl#region ReWriteUrl
private bool ReWriteUrl(HttpContext context)
{
// we're now allowing each individual application to be turned on and off individually. So before we allow
// a request to go through we need to check if this product is disabled and the path is for the disabled product,
// if so we display the disabled product page.
//
// I'm also allowing the page request to go through if the page request is for an admin page. In the past if you
// disabled the forums you were locked out, now with this check, even if you're not on the same machine but you're accessing
// an admin path the request will be allowed to proceed, where the rest of the checks will ensure that the user has the
// permission to access the specific url.
// Url Rewriting
//
//RewriteUrl(context);
string newPath = null;
string path = context.Request.Path;
bool isReWritten = SiteUrls.RewriteUrl(path,context.Request.Url.Query,out newPath);
//very wachky. The first call into ReWritePath always fails with a 404.
//calling ReWritePath twice actually fixes the probelm as well. Instead,
//we use the second ReWritePath overload and it seems to work 100%
//of the time.
if(isReWritten && newPath != null)
{
string qs = null;
int index = newPath.IndexOf('?');
if (index >= 0)
{
qs = (index < (newPath.Length - 1)) ? newPath.Substring(index + 1) : string.Empty;
newPath = newPath.Substring(0, index);
}
context.RewritePath(newPath,null,qs);
}
return isReWritten;
}
#endregion
這個事件主要做兩個事情
a:為發(fā)出請求的用戶初始化一個Context,初始化Context用到了線程中本地數(shù)據(jù)槽(LocalDataStoreSlot),把當(dāng)前用戶請求的上下文(contextb)保存在為此請求開辟的內(nèi)存中。
b:判斷是否需要重寫 URL(檢查是否需要重寫的過程是對SiteUrls.config文件中正則表達式和對應(yīng)Url處理的過程),如果需要重寫URL,就執(zhí)行ASP.NET級別上的RewritePath方法獲得新的路徑,新的路徑才是真正的請求信息所在的路徑。這個專題不是講URL Rewrite,所以只要明白URL在這里就進行Rewrite就可以了,具體的后面專題會敘述。
處理完 Application_BeginRequest 后進程繼向下執(zhí)行,隨后觸發(fā)了Application_AuthenticateRequest(如果有朋友不明白這個執(zhí)行過程,可以通過調(diào)試中設(shè)置多個斷點捕獲事件執(zhí)行的順序。如果你還不會調(diào)試,可以留言偷偷的告訴我,嘿嘿。), Application_AuthenticateRequest事件初始化一個context的Identity,其實CS提供了很多的 Identity支持,包括Microsoft passport,但是目前的版本中使用的是默認值 System.Web.Security.FormsIdentity。具體代碼如下:
private void Application_AuthenticateRequest(Object source, EventArgs e)
{
HttpContext context = HttpContext.Current;
Provider p = null;
ExtensionModule module = null;
// If the installer is making the request terminate early
if (CSConfiguration.GetConfig().AppLocation.CurrentApplicationType == ApplicationType.Installer) {
return;
}
// Only continue if we have a valid context
//
if ((context == null) || (context.User == null))
return;
try
{
// Logic to handle various authentication types
//
switch(context.User.Identity.GetType().Name.ToLower())
{
// Microsoft passport
case "passportidentity":
p = (Provider) CSConfiguration.GetConfig().Extensions["PassportAuthentication"];
module = ExtensionModule.Instance(p);
if(module != null)
module.ProcessRequest();
else
goto default;
break;
// Windows
case "windowsidentity":
p = (Provider) CSConfiguration.GetConfig().Extensions["WindowsAuthentication"];
module = ExtensionModule.Instance(p);
if(module != null)
module.ProcessRequest();
else
goto default;
break;
// Forms
case "formsidentity":
p = (Provider) CSConfiguration.GetConfig().Extensions["FormsAuthentication"];
module = ExtensionModule.Instance(p);
if(module != null)
module.ProcessRequest();
else
goto default;
break;
// Custom
case "customidentity":
p = (Provider) CSConfiguration.GetConfig().Extensions["CustomAuthentication"];
module = ExtensionModule.Instance(p);
if(module != null)
module.ProcessRequest();
else
goto default;
break;
default:
CSContext.Current.UserName = context.User.Identity.Name;
break;
}
}
catch( Exception ex )
{
CSException forumEx = new CSException( CSExceptionType.UnknownError, "Error in AuthenticateRequest", ex );
forumEx.Log();
throw forumEx;
}
// // Get the roles the user belongs to
// //
// Roles roles = new Roles();
// roles.GetUserRoles();
}
再下來是Application_AuthorizeRequest事件被觸發(fā),事件代碼如下:
private void Application_AuthorizeRequest (Object source, EventArgs e) {
if (CSConfiguration.GetConfig().AppLocation.CurrentApplicationType == ApplicationType.Installer)
{
//CSContext.Create(context);
return;
}
HttpApplication application = (HttpApplication)source;
HttpContext context = application.Context;
CSContext csContext = CSContext.Current;
//bool enableBannedUsersToLogin = CSContext.Current.SiteSettings.EnableBannedUsersToLogin;
// // If the installer is making the request terminate early
// if (csContext.ApplicationType == ApplicationType.Installer) {
// return;
// }
//csContext.User = CSContext.Current.User;
CSEvents.UserKnown(csContext.User);
ValidateApplicationStatus(csContext);
// Track anonymous users
//
Users.TrackAnonymousUsers(context);
// Do we need to force the user to login?
//
if (context.Request.IsAuthenticated)
{
string username = context.User.Identity.Name;
if (username != null)
{
string[] roles = CommunityServer.Components.Roles.GetUserRoleNames(username);
if (roles != null && roles.Length > 0)
{
csContext.RolesCacheKey = string.Join(",",roles);
}
}
}
}
在Application_AuthorizeRequest中分析關(guān)鍵幾行代碼:
1:CSContext csContext = CSContext.Current; //該代碼取出在前一個事件中保存在LocalDataStoreSlot中的Context,說明白點就是從內(nèi)存中取出之前保存的一些數(shù)據(jù)。
2: CSEvents.UserKnown(csContext.User); //這里觸發(fā)了一個UserKnown事件,涉及到CS中大量使用委托與事件的一個類CSApplication(CSApplication.cs文件),后續(xù)對這個類做專題分析,這里只要先了解該事件起到判斷登陸用戶是否 ForceLogin以及登錄的帳戶是否是禁用就可以了(把對user的判斷移入Application_AuthorizeRequest事件處理程序中是很好的一種處理方法)
3:ValidateApplicationStatus(csContext); //判斷論壇、blog、相冊是否被禁用,如果登錄用戶的角色不為IsAdministrator,就跳轉(zhuǎn)到相應(yīng)的禁用警告頁面,如Blog被禁用即跳轉(zhuǎn)到 BlogsDisabled.htm頁面顯示。
4:Users.TrackAnonymousUsers(context); //如果是匿名用戶,在這個方法中跟蹤記錄。
處理完上面三個事件后,CS將開始處理請求頁面中的具體業(yè)務(wù)邏輯,如果用戶請求的是登錄頁面,接下來就處理登錄頁面需要的業(yè)務(wù)邏輯和呈現(xiàn),當(dāng)然這里還會觸發(fā)一系列其他事件,因為這些事件沒有在這里定義我們暫時不做考慮。要說明一點,HttpModule在整個web請求到響應(yīng)完成過程中都沒有退出進程,而是處于監(jiān)控狀態(tài)。Application_OnError正是處于其監(jiān)控范圍下的一個事件,一旦有Exception或者繼承Exception的類被異常拋出,HttpModule就捕獲它,之后就可以根據(jù)Exception中ExceptionType值統(tǒng)一處理這些不同的錯誤信息。CS中就是這樣實現(xiàn)錯誤處理的,具體的我們看一下代碼:
private void Application_OnError (Object source, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application = (HttpApplication)source;
HttpContext context = application.Context;
CSException csException = context.Server.GetLastError() as CSException;
if(csException == null)
csException = context.Server.GetLastError().GetBaseException() as CSException;
try
{
if (csException != null)
{
switch (csException.ExceptionType)
{
case CSExceptionType.UserInvalidCredentials:
case CSExceptionType.AccessDenied:
case CSExceptionType.AdministrationAccessDenied:
case CSExceptionType.ModerateAccessDenied:
case CSExceptionType.PostDeleteAccessDenied:
case CSExceptionType.PostProblem:
case CSExceptionType.UserAccountBanned:
case CSExceptionType.ResourceNotFound:
case CSExceptionType.UserUnknownLoginError:
case CSExceptionType.SectionNotFound:
csException.Log();
break;
}
}
else
{
Exception ex = context.Server.GetLastError();
if(ex.InnerException != null)
ex = ex.InnerException;
csException = new CSException(CSExceptionType.UnknownError, ex.Message, context.Server.GetLastError());
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlException sqlEx = ex as System.Data.SqlClient.SqlException;
if(sqlEx == null || sqlEx.Number != -2) //don't log time outs
csException.Log();
}
}
catch{} //not much to do here, but we want to prevent infinite looping with our error handles
CSEvents.CSException(csException);
}
當(dāng)拋出Exception后,CS開始處理Application_OnError,根據(jù)拋出的Exception的ExceptionType類型不同做不同的處理(ForumExceptionType.cs中定義所有的CS ExceptionType)。隨后調(diào)用Log()保存錯誤信息到數(shù)據(jù)庫中,以便管理員跟蹤這些錯誤的原因。這里還有重要的一句:CSEvents.CSException(csException)它觸發(fā)了2個事件類 CSCatastrophicExceptionModule與CSExceptionModule中的處理程序,與 Application_AuthorizeRequest中UserKnown處理機制是一樣的,會在以后的專題討論。只要知道這里會執(zhí)行 RedirectToMessage方法,把頁面重新定向到一個友好的錯誤顯示頁即可,如下圖所示:
至此,CSHttpModule類已經(jīng)全部分析完畢。在CS里還有另外兩個HttpModule,屬于Membership范疇,由于CS引用的是 Membership的程序集無非進行內(nèi)部的運行細節(jié)分析,但是工作原理與CSHttpModule是一致的,當(dāng)你真正理解CSHttpModule的時候要去分析其他HttpModule也就不在話下了。希望我的這些分析能對你有幫助。
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ugoer/archive/2005/09/06/230917.html
AspNet技術(shù):Community Server專題三:HttpModule,轉(zhuǎn)載需保留來源!
鄭重聲明:本文版權(quán)歸原作者所有,轉(zhuǎn)載文章僅為傳播更多信息之目的,如作者信息標(biāo)記有誤,請第一時間聯(lián)系我們修改或刪除,多謝。